- HOME
- HOW IT WORKS
how it works
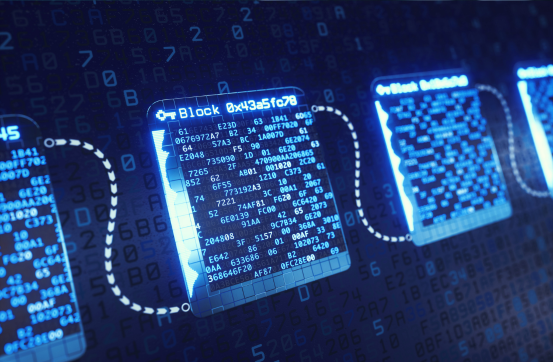
BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY
A blockchain is a innovative technology that has transformed the way we manage and record transactions. It operates as a distributed ledger, enabling the secure and transparent recording of transactions across a network of computers.
At its core, a blockchain utilizes a peer-to-peer network where each computer, known as a node, maintains its own copy of the transaction history. This decentralized approach ensures that no single entity has control over the entire system, enhancing security and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
When a new block of data is added to the blockchain, it becomes the latest version of the entire database. This process involves multiple nodes reaching consensus on the validity of the transaction, ensuring the integrity of the blockchain.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete. The data replication across multiple nodes, combined with a consensus algorithm, safeguards against tampering and ensures the trustworthiness of the information stored on the blockchain.
Encryption plays a crucial role in the security of blockchain technology. Through the use of cryptographic algorithms, sensitive data within transactions is encoded and protected. This ensures that only authorized parties with the appropriate decryption keys can access and interpret the data. Encryption adds an additional layer of security, safeguarding the confidentiality and privacy of the information exchanged within the blockchain network.
By leveraging this innovative technology, businesses across various industries have found numerous applications for blockchains. From financial transactions and supply chain management to digital identity verification and smart contracts, blockchains offer a secure, transparent, and efficient solution for a wide range of use cases.
In conclusion, a blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that revolutionizes the way transactions are recorded and managed. Its decentralized nature, immutability, consensus-driven validation process, and encryption capabilities make it a powerful tool for enhancing security, transparency, and trust in various domains.





